Chinese scientists invent direct electrolysis of seawater, allowing for hydrogen production directly from the ocean using offshore wind energy
China is now able to produce hydrogen directly from the boundless oceans, leveraging the power of renewable energy sources such as offshore wind energy.
Innovation in Seawater Electrolysis

Scientists from Shenzhen University and the Dongfang Electric Innovation Institute (Fujian) have achieved an incredible feat by developing a method called direct seawater electrolysis, which allows them to produce hydrogen directly from the vast oceans using renewable energy sources like offshore wind energy.
Imagine the immense power and untapped potential that lies within our vast oceans, which cover more than 96% of Earth’s water storage. With direct seawater electrolysis, they can harness this colossal resource, extracting hydrogen—a clean and versatile fuel—directly from its depths. It’s like having an infinite energy supply waiting to be unleashed!
Integration with Offshore Wind Energy
But this is where the genius really shines: the scientists have cleverly integrated this technology with offshore wind energy. We all know that offshore wind farms have tremendous renewable energy potential, but utilizing them effectively has been a challenge. By combining the force of ocean waves with direct seawater electrolysis, we can now convert offshore wind energy into hydrogen energy on an impressive scale.

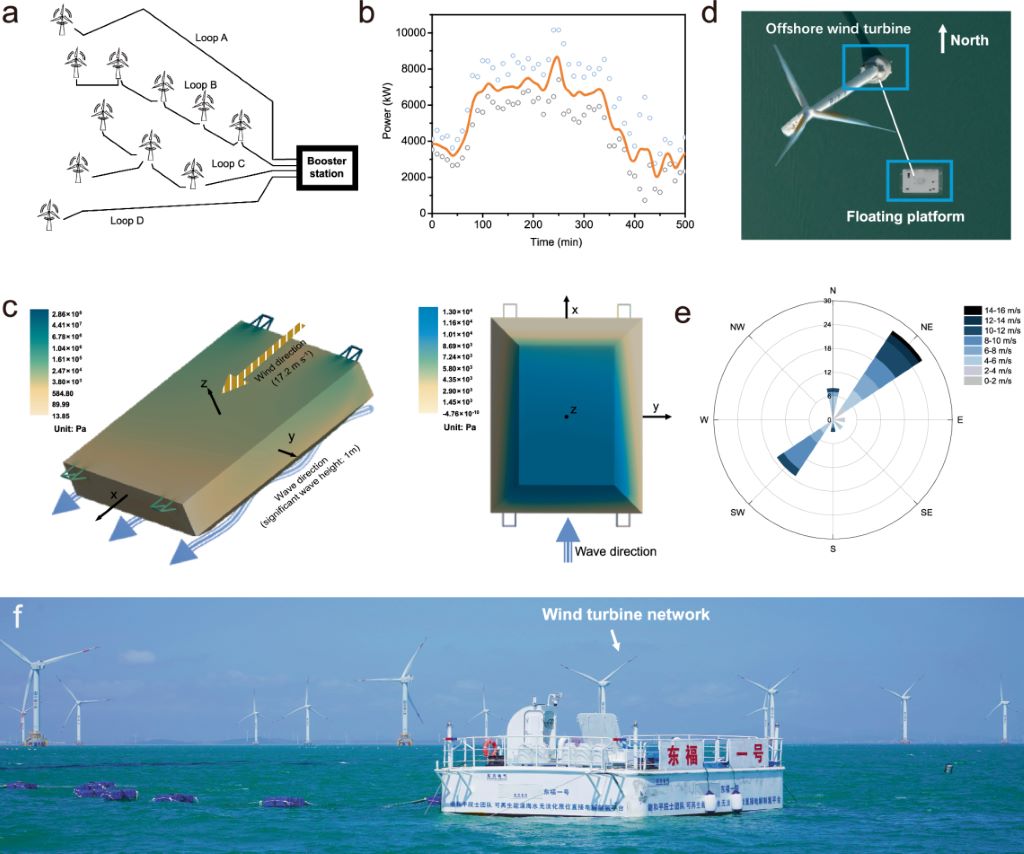
Direct Hydrogen Production The direct production of hydrogen from seawater using renewable energy sources, such as offshore wind energy, has long been touted as a potential solution for achieving a sustainable energy industry. Although laboratory-scale experiments have shown promise, scaling the process and conducting in-situ demonstrations in the unpredictable ocean environment has presented significant challenges.
In this study published in Nature Communications, the team tackled for the first time the fluctuating conditions of the ocean and successfully achieved seawater electrolysis in a wave motion environment. They developed a floating platform equipped with a seawater electrolysis system powered by wind energy. The platform was deployed in Xinghua Bay, and a pilot system of 1.2 Nm³/h scale was integrated for testing.
Impressive Results Remarkably, stable electrolysis operation was achieved for over 240 hours under fluctuating oceanic conditions, including wave heights ranging from 0 to 0.9 meters and wind speeds from 0 to 15 m/s. The system exhibited an electrolytic energy consumption of 5 kWh/Nm³ of H2 and produced high-purity hydrogen (>99.9%), comparable to land-based water electrolysis.
One of the major advantages of this breakthrough is the elimination of the need for pre-desalination processes. Traditional methods of seawater electrolysis often require purification systems to remove impure ions, resulting in increased energy consumption and engineering costs. However, with direct seawater electrolysis, these additional steps are unnecessary, making on-site hydrogen production in the oceans more feasible.
Overcoming Challenges The researchers also addressed the complex composition of seawater, which contains numerous elements that can negatively affect electrolysis. Factors such as the presence of chlorine ions and the deposition of insoluble substances during electrolysis can hinder hydrogen production efficiency. By overcoming these challenges, the team has paved the way for more efficient and reliable direct seawater electrolysis.
Towards a Sustainable Future
The successful demonstration of this floating seawater electrolysis system marks a significant step towards realizing a sustainable energy industry that leverages the vast resources of the world’s oceans. It offers a promising alternative to fossil fuels and provides a pathway to convert offshore wind energy into clean hydrogen energy.
The researchers emphasized the importance of their findings in identifying technological challenges and the performance of key system components. They also highlighted the future prospects of this emerging technology, which could have far-reaching implications for the energy sector and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
This advancement in direct seawater electrolysis shows the potential of harnessing renewable energy sources and utilizing the abundant resources of the oceans to achieve a greener and more sustainable future. Further research and development in this field are expected to improve the efficiency and scalability of the system, bringing us closer to a world powered by clean and renewable hydrogen energy.





















